Glycolysis
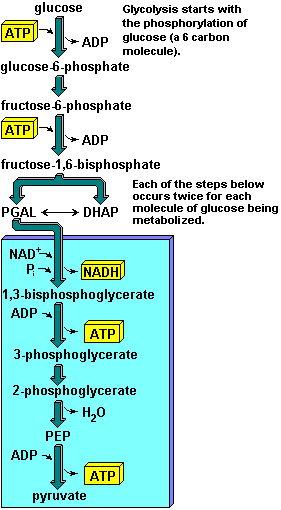
- Glycolysis is the first sequence of reactions
in the breakdown of glucose to obtain energy (from ATP)
- One molecule of 6-carbon sugar (glucose)
plus two ATP molecules
- First of 2 ATPs converts the sugar into gulcose-6-phosphate,
the second forms fructose-1 is split to form 6-biphophate
- 6-biphophate forms two 3-carbon sugar derivatives
- Two 3-carbon sugar derivatives converted
into two molecules of pyruvic acid
- Uses 4 ADP and produces 4 ATP
- The net gain of this process is 2 ATP molecules
(input 2 and output 4 ATPs)
- Once the pyruvic acid is produced there are
two possible pathways, depending
on if oxygen is present
- If glucose is not used immediately it is
converted to glycogen and stored in the muscles
