Krebs/Citric Acid Cycle
For every acetyl group oxidized by this cycle 12
ATP molecules are produced. Overall there are 38 molecules formed
during complete oxidation (through aerobic glycolysis and the
Krebs cycle) of a single glucose molecule.
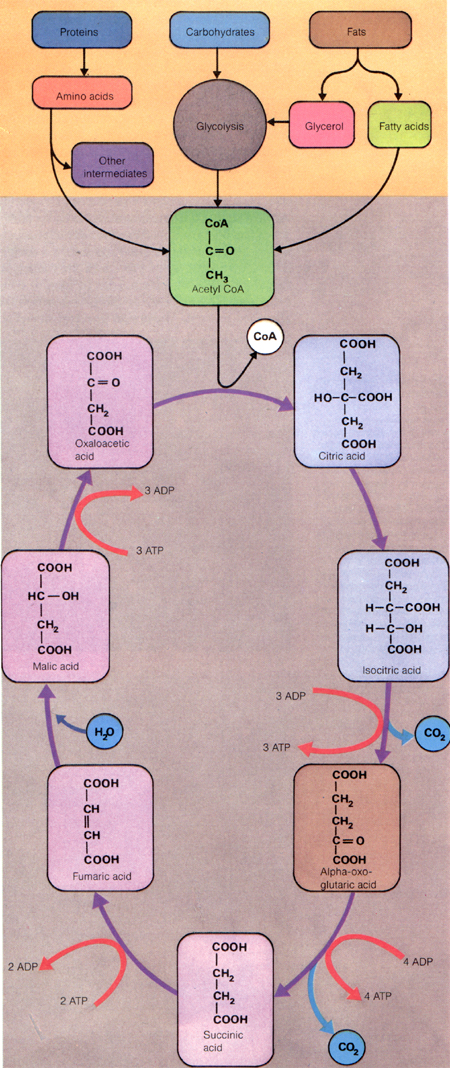
- Acetyl CoA reacts with the compound oxaloacetate
to form citrate and to release coenzyme A (CoA-SH)
- Citrate is rearranged to form isocitrate
which loses a molecule of carbon dioxide
- The isocitrate forms alpha-ketoglutarate,
in the process 3 ATPs are formed as well
- Alpha-ketoglutarate loses a molecule of carbon
dioxide and is oxidized to form succinyl CoA, another 4 ATPs
produced
- This is enzymatically converted to succinate
which is oxidized to fumarate and another 2 ATPs produced
- This is hydrated to produce malate and, to
end the cycle, malate is oxidized to oxaloacetate and 3 ATPs
used and 3 ADPs formed
- Each complete turn of the cycle results in
the regeneration of oxaloacetate and the formation of two molecules
of carbon dioxide
- Cycle repeats and continually producing 12
ATP molecules for every acetyl group oxidized by the cycle

