Chemical Bonding and Energy
Energy can be stored in chemical bonds. The amount of energy in a bond is somewhat counterintuitive - the stronger or more stable the bond, the less potential energy there is between the bonded atoms. Let's repeat that on its own line:
Strong bonds have low potential energy and weak bonds have high potential energy.
Lot's of heat and/or light energy is released when very strong bonds form, because much of the potential energy is converted to heat and/or light energy. The reverse is true for breaking chemical bonds. It takes more energy to break a strong bond than a weak bond. The breaking of a bond requires the absorption of heat and/or light energy.
During a reaction some chemical bonds are broken and new ones are formed. The trick for how a chemical reaction produces energy is to have the new bonds be stronger or more stable than the old bonds. If this is true, some of the potential energy that was present when atoms were more weakly bonded together must be released as heat and/or light to form the new more stable bonds. A chemical reaction happens in several steps:
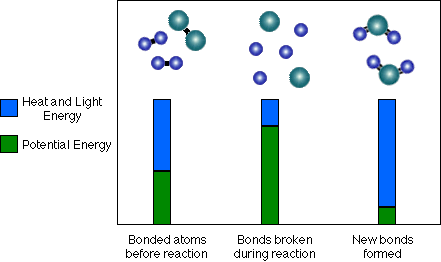
In the example above, the newly bonded atoms often have lower potential energy than the two previously bonded atoms. This means that, after the reaction is done, more of the energy in the system exists as heat or light than before the reaction. See the diagram below of Hydrogen (H-H) and Oxygen (O-O) reacting to form Water (H-O-H):
In chemical notation the reaction is written: 2 H2 + O2 --------------------------------> 2 H2O

Notice that there is more heat and light energy after the new bonds form. In other words, heat and light energy are released as the reaction is completed. On average the bonds in the Water (H-O-H) molecules are stronger than those of the Hydrogen (H-H) and Oxygen (O-O) molecules. Because the (H-O) bonds in water are stronger, they have less potential energy, therefore some of that chemical potential energy must be converted to heat and light.
Also, note that the reaction could be run in reverse, but heat and light energy must be absorbed and converted to chemical potential energy in order to break up water to form Hydrogen and Oxygen.