Chromatography
- Chromatography is a process of separating mixtures.
- In order to perform chromatography you will need the following items:
- Chromatographic column (this is some sort of solid support)
- Solvent (this is often a liquid or a gas in which some mixture is dissolved)
- Mixture
- A mixture by definition is made of more than one substance. Each substance
will have its own set of properties. The substances in a mixture can be separated
if they have differences in their properties. Chromatography uses two different
properties for separation
- Adsorption - the property of how well a substance in the mixture sticks to the chromatographic column. The higher the adsorption the slower the substance will move along the column.
- Solubility - the property of how well a substance in the mixture dissolves into the solvent. The higher the solubility the faster the substance will move along the column.
- By exploiting differences in these two properties we can make the different substances move at different speeds along a chromatographic column by choosing the appropriate solvent and column material.
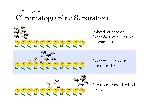
|
|
|
|
|
Explore the Flash plugin below to solidify your understanding
of how chromatography works:
You may want to use these questions
to guide your exploration.
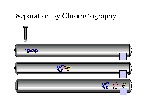
Below is a demo of column chromatography.
Developed in conjunction with the Concord Consortium and with the support
of the National Science Foundation